russia tests 1st atomic bomb impact on cold war|ussr atomic bomb : commercial At a remote test site at Semipalatinsk in Kazakhstan, the USSR successfully detonates its first atomic bomb, code name “First Lightning.” In order to measure the effects of the blast, the . Signo Caliente - Resultados de lotería :: Actual : Sorteos de .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webOs melhores acompanhantes em Marabá - PA. Mais garotas de programas para você. em Marabá - PA. Fikante. Emylly Mel. Jessica. Top. Morena recém chegada na cidade, .
At a remote test site at Semipalatinsk in Kazakhstan, the USSR successfully detonates its first atomic bomb, code name “First Lightning.” In order to measure the effects of the blast, the .This day in history at a remote testing facility in Kazakhstan, the USSR successfully detonates its first atomic bomb. It shocked the world and especially America and the test was a landmark event in the Cold War. The code name .
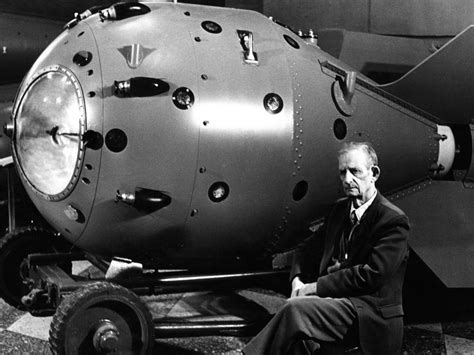
The Soviets successfully tested their first nuclear device, called RDS-1 or “First Lightning” (codenamed “Joe-1” by the United States), at Semipalatinsk on August 29, 1949. As the Cold War intensified, both the . The Soviet Union detonated its first atomic bomb, known in the West as Joe-1, on Aug. 29, 1949, at Semipalatinsk Test Site, in Kazakhstan. It would be another 12 days until, on Sept. 21, U.S. intelligence confirmed to Truman that the Soviets, led by Joseph Stalin, had conducted their first atomic test, which they nicknamed “Joe.
In all, the Soviet Union conducted 456 nuclear tests at Semipalatinsk (340 underground and 116 aboveground), starting with that first one in August 1949 and ending with . On August 29, 1949, the Soviet Union tested its first atomic bomb, sending a mushroom cloud high above northern Kazakhstan and a shadow of fear over the rest of the world.
Drawing on the finding of Tracerlab and other organizations, AFOAT-1 concluded that an atomic bomb had been detonated, that it was a plutonium bomb with a uranium tamper surrounding the pit, and that the date of the test was between .
Following the detonation of Joe-1 in 1949, the Soviets matched the successful U.S. hydrogen bomb test with their own version in 1953, and then more than kept pace as both . Nuclear Bombs and Hydrogen Bombs. A discovery by nuclear physicists in a laboratory in Berlin, Germany, in 1938 made the first atomic bomb possible, after Otto Hahn, Lise Meitner and Fritz .The RDS-1 (Russian: РДС-1), also known as Izdeliye 501 (device 501) and First Lightning (Russian: Пе́рвая мо́лния, romanized: Pyérvaya mólniya, IPA: [ˈpʲervəjə ˈmolnʲɪjə]), [1] was the nuclear bomb used in the Soviet Union's .
But in 1949, the Soviets tested their own atomic bomb, and the Cold War nuclear arms race was on. The United States responded in 1952 by testing the highly destructive hydrogen “superbomb .
Why did the USA Drop an Atomic Bomb on Hiroshima & Nagasaki? The success of the Trinity test in July 1945 meant that the USA were capable of using atomic bombs. The USA dropped two atomic bombs on Japan in August 1945: The first exploded in Hiroshima. The second exploded in Nagasaki. Around 120,000 Japanese civilians were killed by both bombsThe nuclear arms race was an arms race competition for supremacy in nuclear warfare between the United States, the Soviet Union, and their respective allies during the Cold War.During this same period, in addition to the American and Soviet nuclear stockpiles, other countries developed nuclear weapons, though no other country engaged in warhead production on .These comprised the majority (i.e. about 75%) of all nuclear explosions detonated during the Cold War (1945–1989); that is, over 800 of all tests conducted by the United States and nearly 500 of . The Soviet Atomic Bomb and the Cold War On December 25, 1946, the Soviets created their first chain reaction in a graphite structure similar to Chicago Pile-1. After encountering some difficulties with the production of plutonium and the isotopic separation of uranium over the next two years, Soviet scientists managed to get their first .
The Soviet Union detonated its first atomic bomb, known in the West as Joe-1, on Aug. 29, 1949, at Semipalatinsk Test Site, in Kazakhstan. The Soviets called their first atomic test "First Lightning."
The Tsar Bomba was the USSR's response to the nuclear weapons race in the Cold War. But it was far too powerful to use. It was a bomb so big that the USSR wasn't sure that it could test it. The detonation of the world’s first hydrogen bomb, “Ivy Mike,” on November 1, 1952, via The Official CTBTO Photostream It is well-known that the Cold War was an arms race between the United States and the Soviet Union. What is not well-known is the sheer scale of the arsenals of nuclear weapons involved and the absolute power they were able to deliver. The United States detonates the world’s first thermonuclear weapon, the hydrogen bomb, on Eniwetok atoll in the Pacific. The test gave the United States a short‑lived advantage in the nuclear .
On October 30, 1961, the Soviet Union tested the largest nuclear device ever created. The "Tsar Bomba," as it became known, was 10 times more powerful than all the munitions used during World War II.
On 6 August 1945, the USA dropped an atomic bomb close atomic bomb A powerful and destructive bomb that gets its power from the energy released when atoms are split. on the Japanese city of .
This allowed the USSR to test its first nuclear weapon in 1949. 3. During the 1950s, the threat of nuclear weapons was enhanced by new delivery systems. Intercontinental ballistic missiles, for example, could launch nuclear weapons thousands of miles. 4. The first half of the Cold War was marked by a nuclear arms race between the superpowers.The Soviets successfully tested their first atomic weapon on August 29, 1949, after which both superpowers upped the ante by working furiously to develop the far more powerful thermonuclear weapons, or hydrogen bombs. The United .The Russian Federation is known to possess or have possessed three types of weapons of mass destruction: nuclear weapons, biological weapons, and chemical weapons.It is one of the five nuclear-weapon states recognized .
Manhattan Project, U.S. government research project (1942–45) that produced the first atomic bombs. The project’s name was derived from its initial location at Columbia University, where much of the early research was .The United States was not the only leading power on the world stage after the end of World War II; it had a new competitor for this power in the Soviet Union. Tensions between the former allies quickly grew, leading to a new kind of conflict—one heightened with the threat of atomic weapons—that came to dominate global politics for the remainder of the twentieth century.The UK carries out nuclear tests in Western Australia: 1952: The USA successfully tests the first Hydrogen bomb, 2500 times more powerful than the atomic bomb: 1953: The USSR tests its own .
In the 75 years since the first successful test of a plutonium bomb, nuclear weapons have changed the face of warfare. Here, troops in the 11th Airborne division watch an atomic explosion at close . The Soviet Nuclear Program During the Cold War. The Soviet nuclear program that developed the atomic and hydrogen bomb during the early 1950s would continue to expand and accelerate during the Cold War. The U.S.S.R. sought to develop bigger, more powerful bombs to make up for what they perceived to be a disadvantage in the accuracy and .The nuclear arms race was perhaps the most alarming feature of the Cold War competition between the United States and Soviet Union. . the world’s first atomic weapons test in Los Alamos, New .
ussr atomic bomb
At the end of World War II, English writer George Orwell used cold war, as a general term, in his essay "You and the Atomic Bomb", published 19 October 1945 in the British newspaper Tribune.Contemplating a world living in the shadow of the threat of nuclear warfare, Orwell looked at James Burnham's predictions of a polarized world, writing: . Looking at the world as a .
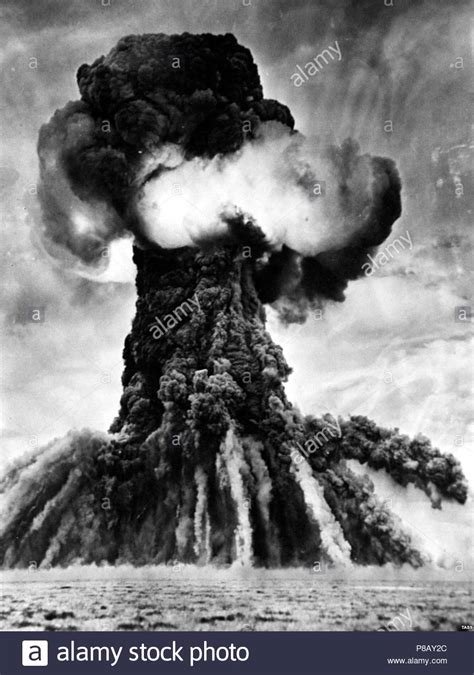

The Truman Administration concluded that only by building up an effective atomic arsenal could it convince the Soviet leaders that they could not continue to prey on struggling nations and provoke another world war. In August 1949, the Soviet Union had tested its first nuclear weapon and was suspected of developing a hydrogen bomb.While the US developed a strategy called "Operation Crossroads" in which they tested how well nuclear explosions performed on battleships, the Soviet Union constructed a domestic supply of uranium and surprised the world by detonating its first atomic bomb in August 1949. At its peak in 1986, the two rivals had nearly 65,000 nuclear warheads between them, making the nuclear arms race one of the most threatening events of the Cold War.
A US Peacekeeper missile launched from a silo Minuteman III launch from Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, United States of America on 9 February 2023.. An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than 5,500 kilometres (3,400 mi), [1] primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more .
eddy current hardness tester india
eddy current hardness testing equipment
webR. Thriller · Action · Crime · Horror. The Devil Comes to Kansas City. 2023. 1 hr 37 min. R. Thriller · Action · Horror. Watch free movies and TV shows online in HD on any device. .
russia tests 1st atomic bomb impact on cold war|ussr atomic bomb